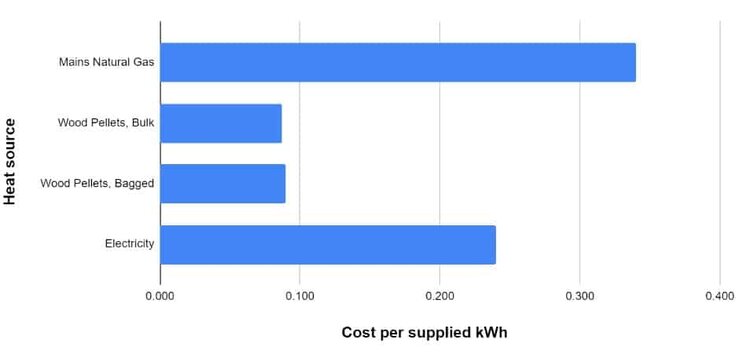
How do wood pellets compare to other fuels?
The use of wood pellets in the energy industry is on the rise worldwide as a replacement for fossil fuels, resulting in a significant reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
A recent study conducted at a power station in the United Kingdom revealed that, despite accounting for fossil fuel emissions throughout the supply chain, including harvesting, manufacturing, and transportation, wood pellets can lower GHG emissions by over 80 percent when compared to coal.
Every type of fuel releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, however, the origin of the fuel plays a significant role in its environmental impact.
For instance, coal is a non-renewable resource that produces more energy compared to biomass. When coal is burned, the high concentration of carbon molecules leads to a greater emission of CO2 per unit of energy.
On the other hand, biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as leftover wood and plant matter. Since wood can be regrown and replenished, the carbon dioxide emitted during its combustion is offset by the regrowth of new vegetation. This makes biomass a renewable energy source that helps in reducing the overall carbon footprint and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Given these factors, woody biomass stands out as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. By utilising biomass energy, we can move towards a cleaner and greener energy transition while reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources like coal. Embracing renewable energy sources like biomass is crucial in our efforts to combat climate change and protect the environment for future generations.
A study concluded that “Pellet stoves provide a modern alternative to wood stoves. They are designed to only burn pelletized wood, from which particle concentrations in the flue gas in the range of 13–81 mg/MJ have been reported consequently lower than in the flue gas from wood stoves.”
A subsequent article also pointed out that pellets show benefits including drastically reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. “Wood pellet fuel reduces greenhouse gas emissions by 54 percent vs. home heating oil, and 59 percent vs. natural gas.”
Utilising wood pellets for heating purposes can result in a carbon emissions reduction of up to 90% in comparison to using oil for heating. By ensuring that the forests providing the wood pellet material are sustainably managed, the overall carbon footprint is greatly minimised when compared to traditional fossil fuel heating methods.